
Paying college with scholarships isn’t as simple as it sounds.
- What are College Scholarships?
- What are the Scholarship Types?
- How do students apply for scholarships?
- When can students apply for portable scholarships?
- How long do scholarships last?
- How do students receive the scholarship money?
- What can you spend scholarship money on?
Let’s start with the definition, scholarships are simply free money for students to spend on their education. This basic definition includes scholarships awarded for pre-schools, dance classes, camps, and, of course, colleges. When you start asking what are scholarships in terms of paying for college, things don’t seem as simple any more. Now you have athletic scholarships, academic scholarships, and other various merit scholarships. And scholarships are just one kind of financial aid available for college so you probably need to have some understanding of how it differs from grants, loans, and work-study. However, even as you wade through various definitions, essentially a scholarship is free money for students to spend on their education.
What are College Scholarships?
When paying for college, scholarships are one of two types of free money that falls under the general description of financial aid. Besides scholarships, students can also receive free money in the form of grants. Financial aid also includes student and parent loans along with work-study.
People new to financial aid often assume that scholarships are based on merit and grants on need. Neither is true. Some of the most generous and prominent scholarships such as The Gates Scholarship require students to have demonstrated need. Furthermore, there are plenty of grants, especially at the graduate level, that are based strictly on the merits of the application.
Why is this important? You may be overlooking valuable scholarships if you limit yourself to these terms.
For our purposes, we’ll continue to use the generic term “scholarship” to refer to free money that students receive for spending on paying for college.
What are the Types of Scholarships?
There are many ways to classify different types of scholarships, merit and need-based is just one way. I think that a more useful grouping for most families is portable or institutional.
Institutional scholarships are those that are limited to students attending the college. I expand this definition to include scholarships that may not be awarded by the institution but are limited only to those attending a specific institution.
Portable Scholarships are those that can be used at more than one college, the scholarship goes where the student goes within certain limitations.
Scholarships in either category can be based on merit or need, require applications or awarded automatically. The point is that students can pursue portable scholarships before they have decided which college to attend.
Examples of scholarship types
Institutional
- Beloit College Presidential Scholarship
- Jefferson Scholarship Program although not administered by the University of Virginia, it can only be used at the University of Virginia.
Portable
- Veterans of Foreign Wars Youth Scholarships
- Peter M. Gargano Scholarship Fund for children of Ulland Brothers employees
How do students apply for scholarships?
For many institutional scholarships, students don’t actually have to do anything other than apply to the college. Many colleges award scholarships based on information students already provide in the application.
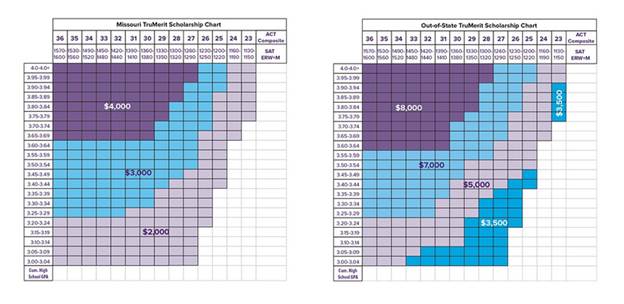
Some of these scholarships are automatic in that students receive specific merit awards based on combinations of test scores, GPA, and class rank. In many cases, the school provides a scholarship calculator or grid so that students can estimate their merit scholarship if admitted. The following is an example for Truman State University.
These scholarships will generally be the largest individual source of scholarship and probably financial aid in general, students receive. This means it’s important for students to consider colleges for merit opportunities when applying. The most competitive colleges in the country generally do not offer any merit scholarships.
Other scholarships such as athletic scholarships or those that require portfolios or auditions don’t actually require a separate application. Students are awarded a scholarship based on their acceptance into the program. There are also a variety of scholarships administered by the university and awarded to students without any other application although based on non-academic criteria. For example: the University of Virginia awards the Bayly-Tiffany Scholarship for undergraduate students who are residents of Accomack or Northampton counties in Virginia.
Many colleges sponsor scholarships that require separate applications. These may be funded by the college or by sponsors that limit the award to students attending the specific college. Such scholarships open to freshman can usually be found on the financial aid webpage. However, some scholarships may only be found in specific departments and limited to certain majors or upper division students.
Applying for Portable Scholarships
There are just about as many ways to apply for portable scholarships as there are scholarships themselves. Depending on your state, students may qualify for scholarships that can be used at public and/or private universities by applying through a state application system. These type of scholarships include the Florida Bright Futures program and the Palmetto Fellows Scholarship of South Carolina. These scholarships often have restriction such as being limited to state residents and must be used at public institutions in state. However, that is not always the case so it’s always a good idea to check. If it doesn’t say one way or another, ask!
There are also community foundations that offer one application form for students to use to apply for a variety of scholarships sponsored locally. Your high school counselor’s office should be able to provide you with information on these types of local opportunities.
Many portable scholarships require the student to apply directly to the sponsoring organization. The organization will have its own application and list any other requirements such as essays, videos, letters of recommendation, and transcripts. Given the variety of deadlines and application requirements, it’s a good idea to use a scholarship tracker to keep everything organized.
When can students apply for portable scholarships?
The most important thing for families to know is that students do not have to be high school seniors to apply for scholarships! Visit JLV Counseling and you’ll see lists of scholarships students can apply to by grade level. Not that you want to have your 13-year-old spending all of her free time applying for scholarships, there’s no reason why she can’t start.
Examples of scholarships for younger students
- Association of Women in Mathematics Essay Contest Open to middles schoolers and up, unspecified monetary award
- Young Filmmakers Contest Grades 3 and up. Up to $1,000 Scholarship
- Scholastic Art & Writing Awards variety of scholarships for grades seven and up.
How long do scholarships last?
The majority of portable scholarships are one-time awards. They are not renewed for each year in college. Often students are allowed to apply to such scholarships only one time. This means that should students find multi-year scholarships, they should give it extra consideration.
Generally institutional merit scholarships are renewable for four-years. They require students to maintain a minimum GPA and take a minimum number of courses each year. Some merit scholarships have relatively high GPA requirements making it difficult for students to keep the scholarship. If students won’t be able to replace the merit scholarship money, they need to be extra diligent in keeping grades up and meeting all requirements.
How do students receive the scholarship money?
he amount of the institutional scholarships are usually applied directly to the amount of tuition and fees owed by the student. The school gives the rest of the money to the student to use on education expenses.
Portable scholarships may be sent directly to the school or they may be awarded to the student. Students who receive the scholarship money directly are required to report the money to the financial aid office and it can affect financial aid. The amount of financial aid students receive cannot exceed the total cost of attendance. This means that students who are receiving need-based aid could potentially have their awards reduced because of outside scholarships. Students need to check with their university to see the maximum of outside awards students can receive before their school reduces their financial aid.
You might be thinking that students just don’t have to report the outside scholarships. Remember, the awarding organization is going to be reporting the information to the IRS for their purposes. So it will show up on the student’s tax return at some point. And if students are receiving need-based aid, the college will eventually see it and there will be problems.
What can you spend scholarship money on?
What you can use scholarship money for can vary according to the organization awarding the scholarship. Generally, scholarships can be used to pay for tuition, fees, and books. Some scholarships will also include room and board.
According to Mark Kantrowitz, there’s really nobody tracking how students spend scholarship money. What students need to keep in mind is that that scholarship money used for tuition, fees, and books is tax free. Whatever students spend on living expenses are taxable. Of course, most college students don’t earn enough money for this to be an issue. But it’s another incentive to prioritize spending scholarship money on education expenses first.



1 thought on “The Complete Scholarship Guide: Everything You Need to Know”